Fake Google Authenticator Malware
Beware of Fake Google Authenticator: A New Info Stealer Malware
In recent times, a dangerous piece of malware disguised as Google Authenticator has been making rounds, posing a significant threat to users. This malicious software is designed to steal sensitive information and exploit user credentials. Here's a breakdown of how this malware operates and what you can do to protect yourself.
The Threat: Fake Google Authenticator
Cybercriminals have created a counterfeit version of Google Authenticator, the legitimate two-factor authentication app. This fake application is cleverly designed to appear as if it's the real deal, but in reality, it's an info stealer. It can be downloaded through deceptive ads that sometimes seem to link to official domains like Google, but instead redirect users to malicious sites.
How the Malware Works
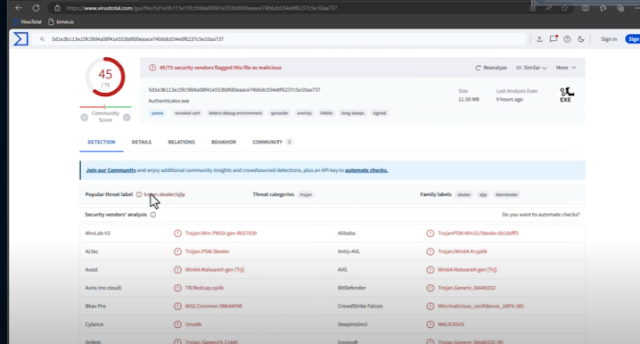
1. **Execution and Network Activity**: Upon execution, this fake authenticator establishes a hidden HTTP connection to a suspicious domain (e.g., vany lo. fun). Monitoring network activity with tools like Fiddler can reveal these unauthorized connections.
2. **Data Theft**: The malware is a variant of an info stealer, specifically a "deer stealer." It intercepts and transmits session cookies and tokens from your browser. This allows attackers to gain access to any sites you're logged into, including sensitive platforms like YouTube.
3. **Malicious Distribution**: The malware can be deceptively distributed through search engine results. A user searching for "Google Authenticator for Windows" might encounter ads that lead to the malicious version of the app. These ads often seem verified and legitimate but are actually part of a sophisticated phishing scheme.
Hosting Platforms and Verification
Interestingly, the malicious executable is often hosted on reputable platforms like GitHub or Google Drive. Attackers exploit these mainstream cloud infrastructures to distribute their malware. While these platforms generally provide a sense of security, they cannot always prevent or monitor every piece of malware uploaded, especially if it's disguised or password-protected.
Digital Signatures and Deception
The fake application may carry a digital signature, which can mislead users into believing it is safe. Although it may not be signed by a trusted entity, some security products might allow it to run based on this signature. This is part of the broader issue where digital verification processes can be circumvented by spending money or using deceptive practices.
Preventive Measures
To avoid falling victim to such attacks, consider the following precautions:
1. **Verify Sources**: Always download software from official websites or trusted sources. Be wary of links and ads, even if they appear to lead to legitimate sites.
2. **Check Digital Signatures**: Be cautious about files with digital signatures. Verify the authenticity of the signature and the source of the file.
3. **Monitor Network Activity**: Use network monitoring tools to detect unusual connections or data transmissions.
4. **Stay Updated**: Keep your security software and operating systems updated to protect against new threats.
Conclusion
The rise of sophisticated phishing techniques and malware distribution through reputable platforms highlights the need for vigilance in digital security. Always scrutinize downloads and links, regardless of how convincing they may seem. Research and cybersecurity professionals continue to combat these threats, but staying informed and cautious is your best defense.
For those seeking to enhance their security posture, tools like Pulseway offer automation and remote monitoring capabilities to manage and protect your systems effectively. Explore solutions that best fit your needs and ensure you stay ahead of potential threats. Stay informed and stay secure!